Isoxaflutole, also known as sulcotrione, is a triketone herbicide developed byFMC Corporation in 1985 and introduced to the market in 1996. It is suitable for controlling annual broadleaf weeds, grass weeds, and sedges in crops such as soybeans, corn, sorghum, peanuts, and sunflowers. Isoxaflutole is particularly effective against sulfonylurea-resistant weeds and is safe for subsequent crops in crop rotation.
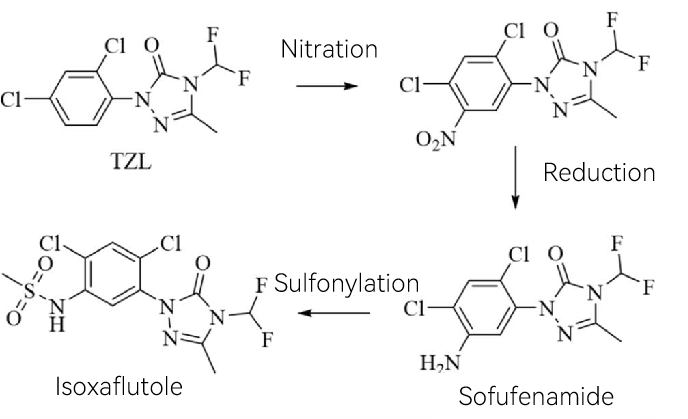
Currently, the primary synthetic route for isoxaflutole is shown in Figure 1. The process begins with the nitration of 2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-difluoromethyl-5-methyl-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazole-3-one (TZL). The resulting nitro compound is then reduced to an amino compound, forming sofufenamide, which undergoes sulfonylation to yield isoxaflutole. This method is relatively simple, features high reaction selectivity, and provides a comparatively high product yield.
YHCHEM SOLUTION
Currently, most industrial production processes utilize batch nitration techniques, in which mixed acid is added dropwise over several hours. This approach results in low production efficiency, large reactor volumes, and high liquid holdup. Furthermore, the limited heat transfer capacity of batch reactors poses significant safety risks. If heat dissipation is not timely, it may lead to uncontrolled boiling in the reactor, causing the reaction to spiral out of control and creating severe safety hazards.
The technical team at YHCHEM has leveraged the characteristics of microchannel reactors, which provide efficient mixing and heat transfer. This makes them well-suited for highly exothermic and hazardous processes such as nitration reactions. The adoption of this technology significantly enhances mixing intensity and ensures intrinsic safety in the process.
Compared with the traditional batch reactor process, the microchannel continuous flow process significantly shortens the reaction time from 2 hours to 57 seconds. The conversion rate of the raw material TZL reaches 100%, the product yield increases from 94% to 96%, and sulfuric acid consumption is reduced by approximately 16%.


