Ароматичні нітросполуки широко використовуються в різних галузях, таких як споживча споживаюча і сільське господарство, біофармацевтична, лаки і фарби, парфумерія та експлозиви. Серед них, 2-нітро-4-метилсульфоніл толуєн є важливим сировинним матеріалом для синтезу гербіциду месосульфурон-метил. Він синтезується за допомогою змішаної кислотної нітрації метилсульфоніл толуєну. Проте, реакції нітрації, будучи швидкими і сильно ексотермічними, складні у створенні локальних гарячих точок під час процесу, що ставить значні безпечнісні ризики. Традиційні партійні реактори не змогли подолати цей виклик.
У останні роки було проведено деякі дослідження нітраційної кінетики різних ароматичних сполук, таких як толуєн, нітротолуєн, та хлоробензоль. Проте, досліджень нітрації метилсульфоніл толуєну дуже мало. Під час нітрації метилсульфоніл толуен має дифундувати з органічної фази в водну фазу і реагувати з іоном нітронію (NO₂⁺), що утворюється за допомогою реакції концентрованої HNO₃ і H₂SO₄. Цей процес зустрічає значну опору масопередачі. Тому, для отримання точних кінетичних даних, потрібна методика зупинки реакції нітрації протягом мілісекунд, а також пристрій з відмінними характеристиками масопередачі та теплопередачі.
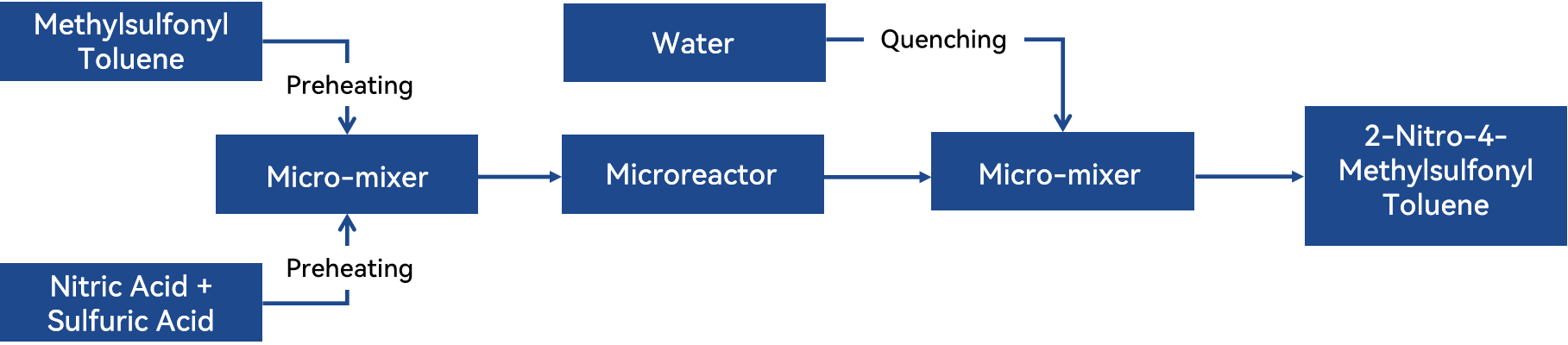
YHCHEM SOLUTION
Неперервний потоковий мікрореактор, розроблений YHCHEM незалежно, має переваги, такі як ефективна масопередача та теплопередача, невеликий об'єм реакції та короткий час задержки. Він дозволяє точно керувати температурою реакції та часом. У kombінації з мікро-мішачим пристроєм і модулями високої точності ця система ефективно вирішує викликані проблеми під час процесу нітрації метилсульфоніл толuenу. Конкретний процес показано на схемі нижче.